How Does A System At Equilibrium Respond To The Addition Of More Reactant
How does a system at equilibrium respond to the addition of more reactant. A body is in state of equilibrium if all the forces acting on the body is equal to zero. Not affect the equilibrium. If we add additional product to a system the equilibrium will shift to the left in order to produce more reactants.
Chemical equilibria can be shifted by changing the conditions that the system experiences. How does a system at equilibrium respond to the addition of more reactant. Le Chateliers Principle is the principle when a stress is applied to a chemical system at equilibrium the equilibrium will shift to relieve the stressIn other words it can be used to predict the direction of a chemical reaction in response to a change in conditions of temperature concentration volume or pressureWhile Le Chateliers principle can be used to predict the response to a.
What factors increase the rate of a chemical reaction. When is equilibrium established in a reversible reaction. The system will subsequently experience a net reaction in the direction of greater rate a shift that will re-establish the equilibrium.
It does so by removing the added reactant increasing the rate of the forward reaction and making more product until the equilibrium proportions are re-established. If an equilibrium system is subjected to a change in conditions that affects these reaction rates differently a stress then the rates are no longer equal and the system is not at equilibrium. Addition of reactants or products in the case of the reverse reaction to a system at equilibrium disturbs that equiliibrium.
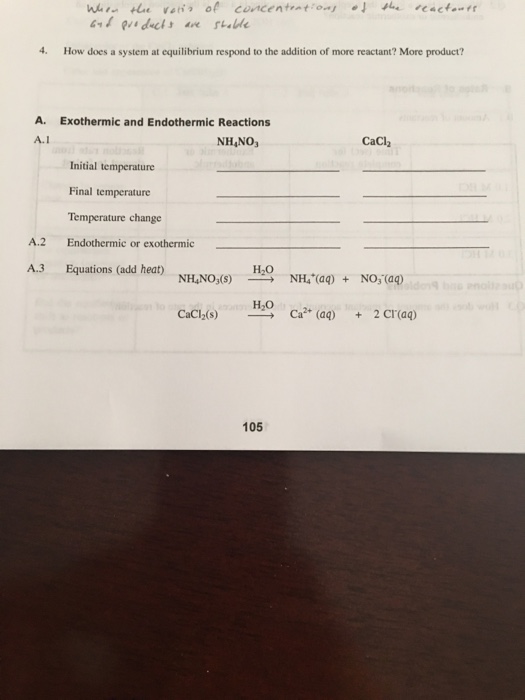
And we add more of A then the equilibrium constant for the new final final state will remain as it was ceteris paribus. Show transcribed image text 20171011 114543 jpy- Pholos Pre-Lab Study Questions How does an exothermic reaction differ from an endothermic reaction. If all the forces acting along horizontal direction and in vertical direction cancel the effect of each other the body is said to be in state of equilibriumSummation of forces 0The second condition of equilibrium is that the net torque acting on.
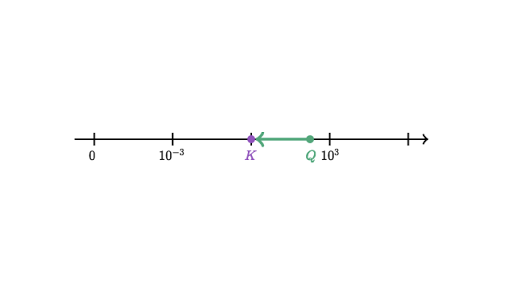
Answer 1 of 1. How does a system at equilibrium respond to the addition of more reactant. What am I getting wrong because my textbook suggests that K will always increase no matter what type of reaction I am dealing with of course as long as all.
Certainly if we have a simple reaction. - This means the equilibrium will shift to the right.
Click to see full answer.
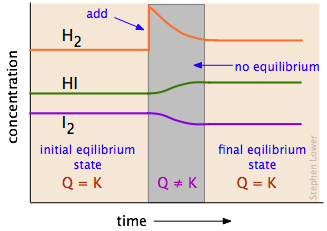
If an equilibrium system is subjected to a change in conditions that affects these reaction rates differently a stress then the rates are no longer equal and the system is not at equilibrium. How does an equilibrium reaction. The system responds in such a way as to re-establish the equilibrium. What factors increase the rate of a chemical reaction. There are two conditions of equilibrium. And we add more of A then the equilibrium constant for the new final final state will remain as it was ceteris paribus. How does a system at equilibrium respond to the addition of more product. If the concentration of a substance is increased the reaction shifts to consume the excess substance. A body is in state of equilibrium if all the forces acting on the body is equal to zero.
Addition of reactants or products in the case of the reverse reaction to a system at equilibrium disturbs that equiliibrium. If we add additional product to a system the equilibrium will shift to the left in order to produce more reactants. And we add more of A then the equilibrium constant for the new final final state will remain as it was ceteris paribus. SO2 g Cl2 g SO2Cl2 g Add 1 mol of Ne g will. It does so by removing the added reactant increasing the rate of the forward reaction and making more product until the equilibrium proportions are re-established. Click to see full answer. As temperature increases the rate of the reaction increases as well because it allows atoms to move faster.


































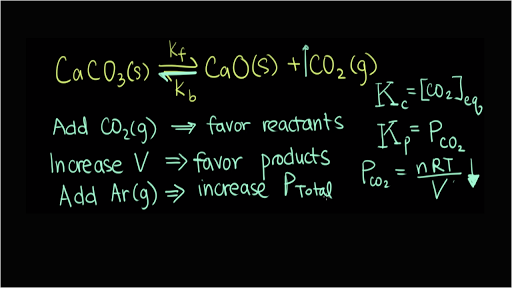







Post a Comment for "How Does A System At Equilibrium Respond To The Addition Of More Reactant"